How to Calculate ROI for a Project
When kicking off a new project, an important question you might ask is, "Is this investment worth the time, money, and effort that will go behind it?" Calculating the Return on Investment (ROI) answers that critical question and paves the way for a clearer financial journey for your project.
ROI is a common business term for a good reason. Viewed through a financial lens, it serves as a crucial metric to determine whether your project is worth pursuing. Whether you're a startup founder, project manager, or marketer, ROI analysis empowers you to make well-informed decisions. It provides a clear and simple perspective on your project's potential or actual profitability.
This guide is all about calculating ROI for different projects, like fixed price, time & materials, and recurring revenue. You'll learn how to figure out ROI, and use it to make your projects more profitable.
Understanding ROI Basics
Return on Investment, or ROI, is your financial compass—it tells you whether the money you're putting into a project is turning into profit. In simple terms, ROI measures the efficiency and profitability of an investment. It answers a straightforward question: for every dollar invested, how much money are you getting back?
Broadly speaking, there are two types of ROI you'll encounter:
- Anticipated ROI: This is calculated before your project starts. It's based on your projections of costs and revenue, and it helps you decide whether the project is worth pursuing.
- Actual ROI: This is calculated after your project ends. It uses real numbers to show you how much profit the project actually generated.
Both types are crucial. Anticipated ROI helps in making the decision to start a project, while actual ROI provides a clear picture of the project's financial success.
Now, you might wonder: if your project seems sound in all technical aspects, should you really bother getting into ROI calculations?
Well, yes. Understanding ROI is critical because:
- It helps you make informed decisions about which projects to pursue.
- It allows you to assess the financial health of ongoing and completed projects.
- It enables you to justify project expenditures to stakeholders.
ROI isn't a mere number—it's a projection (no pun intended) of your project's success and a guide for future investments. Whether you're deciding to launch a new project or evaluating the performance of an ongoing one, a clear understanding of ROI provides a pathway to more strategic and profitable decisions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating ROI
With the basic concept crystal clear, let’s look at how to calculate return on investment for different types of projects. There are three key steps involved in evaluating a project’s ROI:
1. Initial Setup and Data Collection
Start by listing all the costs involved in your project. This includes everything from direct costs like materials and labor to indirect costs such as administrative and ad spending. Being thorough in this step sets the stage for an accurate ROI calculation.
Next, estimate the financial value your project will generate. This could be direct income from sales or less tangible benefits like cost savings from increased efficiency. Your revenue vs income estimates should be based on realistic, well-researched assumptions to ensure your anticipated ROI is grounded in reality.
2. Calculating Net Profit
Net profit is what you have left after subtracting the total expenditure from your expected revenues.
So:
- Calculate your total expenses.
- Estimate your total expected revenues.
- Subtract the total expenses from your expected revenues to determine your net profit.
For example, if you expect to generate $10,000 in revenue from a project that costs $7,000 to execute, your net profit would be:
Net Profit = Total Revenue−Total Expenses = $10,000−$7,000 = $3,000
Next, put this into the ROI formula.
3. Applying the ROI Formula
Once you have your net profit, apply the ROI formula:
ROI = (Net Profit/Cost of Investment)×100
Using the example above, ROI = ($3000/$7000)×100 = 42.86%
This gives you the basic ROI calculation.
However, the method we use can change based on the nature of the project at hand. Let’s explore how to tailor your ROI calculation for various project types: Fixed Price, Time & Materials (T&M), and Recurring Revenue.
Fixed Price Projects
In fixed price projects, the budget and revenue are agreed upon before the project begins, making financial calculations more straightforward.
ROI = (Fixed Project Cost/Net Profit)×100
So, suppose you have a marketing campaign where the client pays $20,000, and the agreed campaign costs are $15,000.
Then, Net Profit = $20,000−$15,000 = $5,000
ROI = ($5,000/$15,000)×100 = 33.33%
Time & Materials Projects
These projects bill clients based on the actual time spent and materials (T&M) used. This model requires meticulous tracking of all expenses and hours worked.
Calculating ROI for these projects can be a tad trickier as revenue and costs vary. Here’s how to do it:
- Track billable hours accurately and ensure to account for all labor costs.
- Keep a record of the resources you used for the project and their costs.
- Estimate the net profit as the total billable hours minus labor costs and materials.
- Calculate the project’s ROI using the formula above.
So, say you have a project where billable hours and materials amount to $30,000 in revenue, with labor and materials costing $22,000.
Then, Net Profit = $30,000−$22,000 = $8,000
ROI = ($8,000/$22,000)x100 = 36.36%
Recurring Revenue Projects
Common in services and subscriptions, these projects generate revenue over a period of time, requiring an ongoing assessment of profitability.
Here, ROI is typically assessed per period (monthly, quarterly), and might also consider the customer lifetime value for longer-term assessments:
ROI = (Periodic Net Profit/Periodic Costs)x100
For instance, a software-as-a-service (SaaS) product generates $10,000 in monthly revenue from its users and incurs $6,000 in ongoing costs (servers, hosting, customer service, etc.).
Then, Net Profit = $10,000−$6000 = $4,000
Monthly ROI = ($4,000/$6,000)x100 = 66.67%
By customizing the ROI formula to fit the project type, you ensure that your profitability calculations are accurate and reflective of your actual business operations. These examples illustrate how ROI calculations must adapt to different project dynamics, so you have a reliable metric to gauge the financial success of your projects.
Monitoring and Adjusting ROI
Okay, back to some theory in this section.
As your project kicks off, it's really important to keep a friendly eye on your costs and revenues. By watching these numbers, you'll get a clearer picture of how they match up with your original estimates. This ongoing check-in helps you spot trends and make timely tweaks, keeping your project on the right path to reach those financial goals you've set.
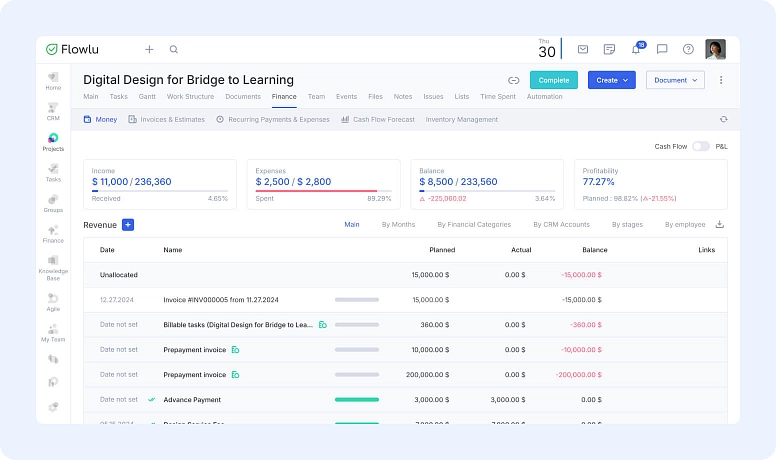
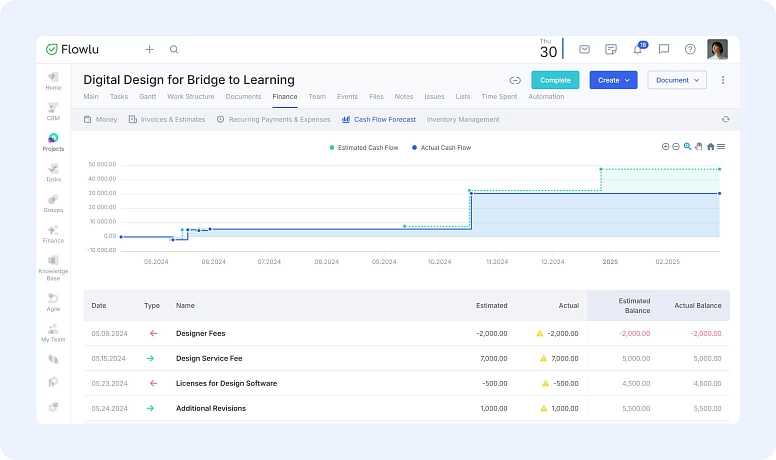
Feel free to tweak your forecasts if you spot any differences between your projected and actual figures. This could involve updating your revenue expectations in light of new market conditions or exploring ways to cut costs while still maintaining quality. Using a tool like Flowlu makes this process easier by automatically tracking project expenses, revenues, and ROI in real time, so you can make adjustments based on actual data instead of guesswork. By regularly updating your ROI projections, you can better manage stakeholder expectations and ensure your project stays financially healthy.
Interim ROI calculations can also provide critical insights into project performance before it's completed. These early insights allow you to pivot or change strategies if the project isn't meeting financial goals. For example, if an ROI calculation halfway through the project shows a lower-than-expected return, you can investigate causes and implement changes to improve profitability.
Suppose after the first quarter, your project's actual revenues are only $7,000 compared to an anticipated $10,000, while costs are as expected. You might need to boost marketing efforts or reevaluate the project scope to ensure the final ROI meets your targets.
Post-Project ROI Analysis
Once your project wraps up, it's time to calculate the actual ROI. This involves using the real revenue and cost figures accrued during the project. Actual ROI provides a definitive measure of how financially successful your project was compared to your initial predictions.
Just like with anticipated ROI, apply the same formula:
Actual ROI = (Actual Cost of Investment/Actual Net Profit)×100
Comparing anticipated vs. actual ROI is vital. It helps you understand where your projections were accurate and where they may have fallen short. Analyzing these differences can provide two valuable lessons:
- If the actual ROI is lower than anticipated, investigate areas where costs may have overrun or revenue fell short.
- If the actual ROI is higher, determine which efficiencies or market advantages contributed to this success.
Take the insights from your ROI analysis to fine-tune your approach for future projects. By grasping what went well and what could be improved, you’ll be able to create even better financial models and make more thoughtful decisions in your upcoming ventures.
And remember, it’s really helpful to compile your findings into a report and share it with your stakeholders. This report should highlight the project's financials, showcase how effective the investment was, and offer recommendations for future projects based on the valuable ROI results.
Challenges and Best Practices in ROI Calculation
Calculating ROI seems straightforward, but there are common challenges that can skew your results:
- Overestimating Revenue: Optimism is great, but realistic, data-backed forecasts are better. Overestimation can lead to disappointing ROI figures and misguided expectations.
- Underestimating Costs: Projects often run over budget. Always include a buffer for unexpected costs to avoid unpleasant surprises.
- Ignoring External Factors: Economic shifts, market trends, and competitive actions can all impact your project's financials. Stay agile and ready to adapt your strategies in response to these changes.
Moreover, to ensure your ROI calculations are as reliable as possible, put the following tips into practice:
- Keep detailed records of all financial transactions related to the project. Thorough documentation helps with accurate calculations and simplifies audits.
- Conduct financial reviews at set intervals throughout the project to catch deviations early and adjust plans accordingly.
- Stick to industry-standard formulas for ROI to maintain consistency and comparability across projects.
- Involve key stakeholders in the ROI planning and review process. Their insights can provide additional context and help refine your projections.
- Modern project management and financial analysis tools like Flowlu automates data tracking and calculations, reducing errors and saving time. You get clear dashboards that present data visually, making it easier to interpret and share insights.
So, this is how things would look if you apply these best practices: say you’re heading a project team, use a standardized ROI formula, and conduct monthly financial reviews. You adjust your new website launch project plan after realizing that one of your key resources—the content management system (CMS) your website would be running on—was more expensive than planned. By conducting a thorough CMS comparison, you switch to the right CMS platform and manage to save 15% on projected costs, positively impacting your final ROI.
Considerations for Complex Projects
Not all projects are created equal, and some involve complexities that standard ROI calculations may not fully capture. For complex projects, consider these advanced considerations:
- Risk-adjusted ROI: Factor in the probability of various outcomes to adjust the ROI calculation for risk. This approach requires a more nuanced view of potential returns, considering the uncertainties involved.
- Long-term ROI: Some projects, especially in sectors like construction or technology, have long-term benefits that aren't always immediately apparent. Extend your ROI analysis over a longer period to capture these extended benefits.
- Intangible benefits: Projects may have intangible benefits, such as better brand awareness, that are difficult to quantify but have real value. Develop methods to assign monetary or numerical values to these intangibles for a more comprehensive ROI.
Also, ROI analysis shouldn't exist in a vacuum. Integrate it with broader business intelligence (BI) systems, such as advanced data analytics platforms, to gain deeper insights and more accurately predict ROI under complex scenarios. Implement dashboards that visualize ROI alongside other key performance indicators (KPIs). This holistic view helps align project outcomes with business objectives.
Closing Thoughts
Ultimately, you can use ROI not just as a measure of past performance but as a strategic tool for future planning. Analyze the ROI of various projects and create feedback loops to determine which types should receive more investment. This strategic approach means you allocate resources more effectively with every new project, enhancing your overall business performance in a continuous improvement cycle.
ROI (Return on Investment) helps you figure out if a project is worth the time, effort, and money. It shows if you're likely to make a profit or just break even. It also helps you keep an eye on project costs and explain spending to others.
It’s a simple formula:
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) × 100
The tricky part is making sure you count all costs and expected income correctly. The approach depends on the type of project:
- Fixed Price – Costs and income are agreed on upfront.
- Time & Materials – You charge based on work done and materials used, so costs and income change as you go.
- Recurring Revenue – Think of subscription-based businesses where profits build up over time.
Common mistakes include guessing income too optimistically, forgetting about hidden costs, and ignoring things like market changes or competition. The best way to stay on track is to keep good records, check numbers regularly, and adjust your estimates as needed.